Human Mastication Analysis: A DEM Based Numerical Approach
Abstract
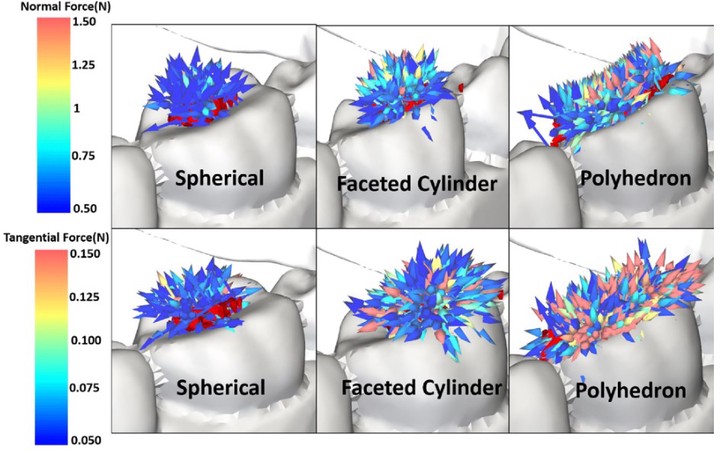
Mastication is an essential and preliminary step of the digestion process involving fragmentation and mixing of food. Controlledmuscle movement of jaws with teeth executes crushing, leading towards fragmentation of food particles. Understanding variousparameters involved with the process is essential to solve any biomedical complication in the area of interest. However, exploringand analyzing such process flow through an experimental route is challenging and inefficient. Computational techniques suchas discrete element numerical modeling can effectively address such problems. The current work employs the Discrete ElementMethod (DEM) as a numerical modeling technique to simulate the human mastication process. Tavares and Ab-T10 breakagemodels coupled with Gaudin Schumann and Incomplete Beta fragment distribution models have been implemented to analyzethe fragmental distribution of food particles. The effect of particle shape (spherical, polyhedron, and faceted cylinder), size (as-pect ratio), and orientation (vertical and horizontal) on breakage and fragment distribution is analyzed. To account for the elas-tic–plastic behavior and moisture content in food particles, modifications has been made in breakage models by incorporatingnumerical softening factor and adhesion force. The study demonstrates how numerical modeling techniques can be utilized toanalyze the mastication process involving multiple process parameters.